前端控制器(DispatcherServlet)的架构
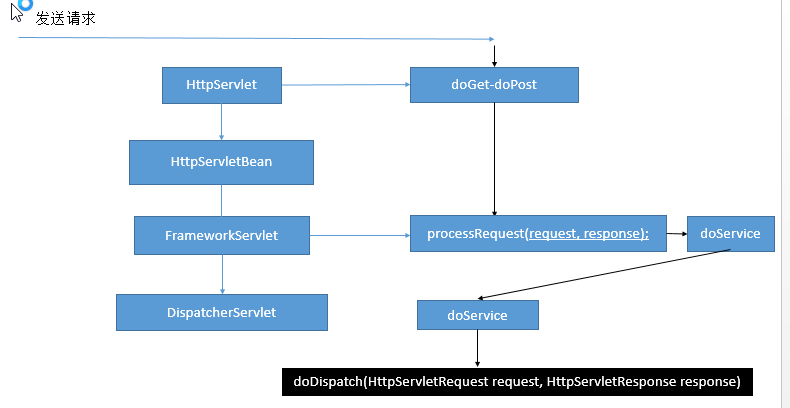
FrameworkServlet中的doService是一个抽象类,具体的实现在DispatcherServlet
protected abstract void doService(HttpServletRequest var1, HttpServletResponse var2) throws Exception;
DispatcherServlet中的doService着重看这一段
try {
this.doDispatch(request, response);
} finally {
doDispatch细节
protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request;
HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null;
boolean multipartRequestParsed = false;
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
try {
try {
ModelAndView mv = null;
Object dispatchException = null;
try {
--
//1、检查是否文件上传请求
--
processedRequest = this.checkMultipart(request);
multipartRequestParsed = processedRequest != request;
--
//2、根据当前的请求地址找到那个类能来处理;
--
mappedHandler = this.getHandler(processedRequest);
--
//3、如果没有找到哪个处理器(控制器)能处理这个请求就404,或者抛异常
--
if (mappedHandler == null) {
this.noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response);
return;
}
--
//4、拿到能执行这个类的所有方法的适配器;(反射工具AnnotationMethodHandlerAdapter)
--
HandlerAdapter ha = this.getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler());
String method = request.getMethod();
boolean isGet = "GET".equals(method);
if (isGet || "HEAD".equals(method)) {
long lastModified = ha.getLastModified(request, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if ((new ServletWebRequest(request, response)).checkNotModified(lastModified) && isGet) {
return;
}
}
if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) {
return;
}
--
// Actually invoke the handler.处理(控制)器的方法被调用
//控制器(Controller),处理器(Handler)
//5、适配器来执行目标方法;将目标方法执行完成后的返回值作为视图名,设置保存到ModelAndView中
//目标方法无论怎么写,最终适配器执行完成以后都会将执行后的信息封装成ModelAndView
--
mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
return;
}
this.applyDefaultViewName(processedRequest, mv);
mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv);
} catch (Exception var20) {
dispatchException = var20;
} catch (Throwable var21) {
dispatchException = new NestedServletException("Handler dispatch failed", var21);
}
--
//转发到目标页面;
//6、根据方法最终执行完成后封装的ModelAndView;转发到对应页面,
而且ModelAndView中的数据可以从请求域中获取
--
this.processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, (Exception)dispatchException);
} catch (Exception var22) {
this.triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, var22);
} catch (Throwable var23) {
this.triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, new NestedServletException("Handler processing failed", var23));
}
} finally {
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
if (mappedHandler != null) {
mappedHandler.applyAfterConcurrentHandlingStarted(processedRequest, response);
}
} else if (multipartRequestParsed) {
this.cleanupMultipart(processedRequest);
}
}
}
基本流程:
1. 所有请求过来DispatcherServlet收到请求,
2. 调用doDispatch()方法进行处理
1.getHandler():根据当前请求地址找到能处理这个请求的目标处理器类(处理器)
根据当前请求在HandlerMapping中找到这个请求的映射信息,获取到目标处理器类
2.getHandlerAdapter():根据当前处理器类获取到能执行这个处理器方法的适配器;
根据当前处理器类,找到当前类的HandlerAdapter(适配器)
3. 使用刚才获取到的适配器(AnnotationMethodHandlerAdapter )执行目标方法;
4.目标方法执行后会返回一个ModelAndView对象
5.根据ModelAndView的信息转发到具体的页面,并可以在请求域中取出ModelAndView中的模型数据
getHandler细节
SpringMVC怎么根据当前请求就能找到哪个类能来处理?
mappedHandler = this.getHandler(processedRequest);//放行
getHandler()会返回目标处理器类的执行链;

step into:
protected HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
if (this.handlerMappings != null) {
Iterator var2 = this.handlerMappings.iterator();
while(var2.hasNext()) {
HandlerMapping mapping = (HandlerMapping)var2.next();
HandlerExecutionChain handler = mapping.getHandler(request);
if (handler != null) {
return handler;
}
}
}
return null;
}
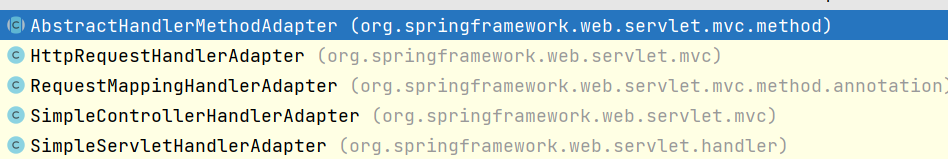
HandlerMappings有什么?
HandlerMappings:处理器映射,他里面保存了每一个处理器能处理哪些请求的映射信息
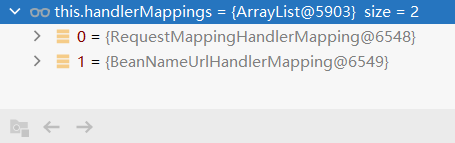
与Spring4.0的对比
![Image [2]](/upload/2022/10/Image%20%5B2%5D.png)
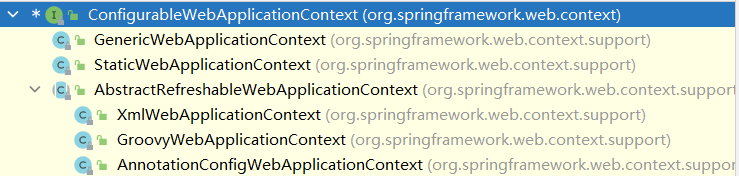
SpringMVC如何存储映射信息?
mappingLookup:ioc容器启动创建Controller对象的时候扫描每个处理器都能处理什么请求,保存在HandlerMapping的mappingLookup属性中;
下一次请求过来,就来看哪个HandlerMapping中有这个请求映射信息就行了;
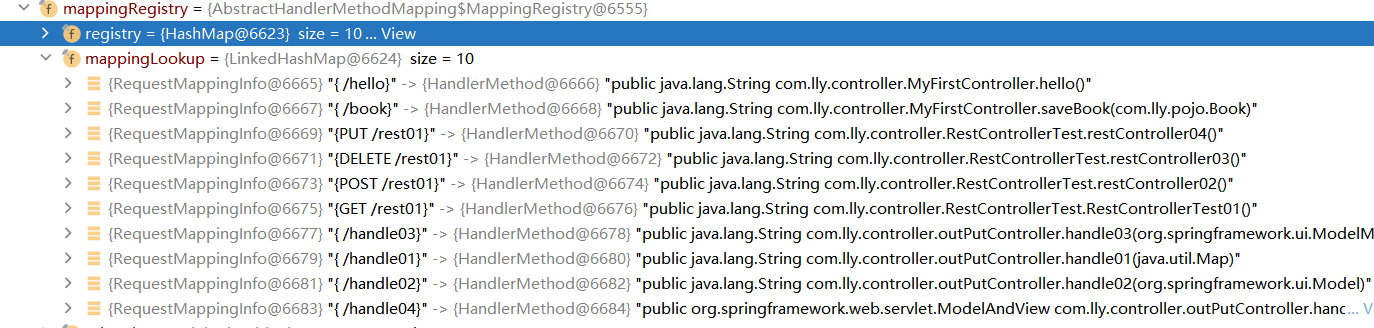
与Spring4.0的对比
![Image [3]](/upload/2022/10/Image%20%5B3%5D.png)
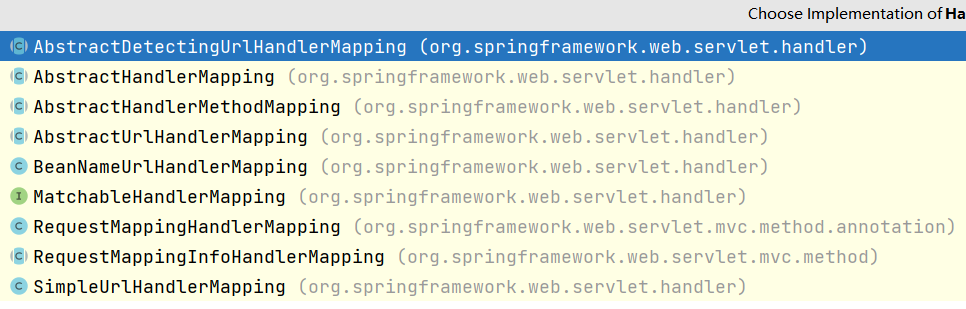
个人补充:
与4版本相比,同样是使用注解的方式编写controller,但4版本中的DefaultAnnotationHandlerMapping
在5版本中是没有的了,如下图:
被替换成RequestMappingHandlerMapping
由前面还可以知道BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping的顺序也放在了后面。
留个坑:在看SpringBoot源码的时候貌似SimpleUrlHandlerMapping也会出现在HandlerMappings中,
==
这里却没有
--
getHandlerAdapter细节
如何找到目标处理器类的适配器。要拿适配器才去执行目标方法?
HandlerAdapter ha = this.getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler());
step into:
protected HandlerAdapter getHandlerAdapter(Object handler) throws ServletException {
if (this.handlerAdapters != null) {
Iterator var2 = this.handlerAdapters.iterator();
while(var2.hasNext()) {
HandlerAdapter adapter = (HandlerAdapter)var2.next();
//查看哪个适配器支持传入得处理器
if (adapter.supports(handler)) {
return adapter;
}
}
}
throw new ServletException("No adapter for handler [" + handler + "]: The DispatcherServlet configuration needs to include a HandlerAdapter that supports this handler");
}
SpringMVC 5.0版本
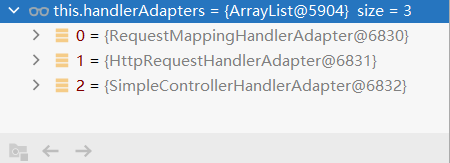
与SpringMVC4.0的对比:
![Image [4]](/upload/2022/10/Image%20%5B4%5D.png)
与HandlerMapping一样,在Annotationxxx什么的换成了RequestMappingHandlerAdapter
结合Spring流程看SpringMVC
1. Spring在启动的时候,进行WebApplicationContext的初始化,首先会逐个加载你配置的xml文件,然后第二个。。。
@Override
public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent event) {
initWebApplicationContext(event.getServletContext());
}
2.进入ContextLoader的initWebApplicationContext方法,节约空间源码只留一部分
public WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext(ServletContext servletContext) {
try {
--
//传入的servletContext的context为空,直接创建一个WebApplicationContext
//至于servletContext的context为什么会有东西,可以追溯下源码,
//public ServletContext getServletContext () { return (ServletContext) super.getSource(); }
//这是一个事件类,用于通知web应用程序的servlet上下文的更改.自: Servlet 2.3 参见: ServletContextListener
//其从源文件中getSource返回一个ServletContext,其中带有context,再深入的东西暂时不研究
--
if (this.context == null) {
this.context = createWebApplicationContext(servletContext);
}
--
如果类型是ConfigurableWebApplicationContext的,将这个类型的context进行向上转型,
this.context此时的类型是XmlWebApplicationContext
--
if (this.context instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) {
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) this.context;
if (!cwac.isActive()) {
if (cwac.getParent() == null) {
ApplicationContext parent = loadParentContext(servletContext);
cwac.setParent(parent);
}
--
配置和刷新Web应用程序上下文,step into
--
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac, servletContext);
}
}
servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, this.context);
ClassLoader ccl = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();
if (ccl == ContextLoader.class.getClassLoader()) {
currentContext = this.context;
}
else if (ccl != null) {
currentContextPerThread.put(ccl, this.context);
}
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
long elapsedTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime;
logger.info("Root WebApplicationContext initialized in " + elapsedTime + " ms");
}
return this.context;
}
catch (RuntimeException | Error ex) {
logger.error("Context initialization failed", ex);
servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, ex);
throw ex;
}
}
3.configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext
protected void configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext wac, ServletContext sc) {
if (ObjectUtils.identityToString(wac).equals(wac.getId())) {
String idParam = sc.getInitParameter(CONTEXT_ID_PARAM);
if (idParam != null) {
wac.setId(idParam);
}
else {
// Generate default id...
wac.setId(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ID_PREFIX +
ObjectUtils.getDisplayString(sc.getContextPath()));
}
}
wac.setServletContext(sc);
--
//获取配置文件位置参数
//首先获取的是applicationContext.xml
//
--
String configLocationParam = sc.getInitParameter(CONFIG_LOCATION_PARAM);
if (configLocationParam != null) {
wac.setConfigLocation(configLocationParam);
}
.....
customizeContext(sc, wac);
--
//调用refresh方法进行容器的刷新
--
wac.refresh();
}
4.refresh方法
wac的类型被转成是ConfigurableWebApplicationContext(接口)
但原本类型还是XmlWebApplicationContext
其继承关系:
–
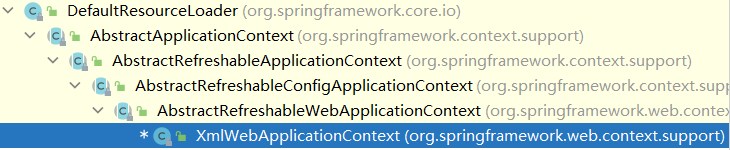
refresh方法在AbstractApplicationContext有实现,所以跳到AbstractApplicationContext中执行以下代码。
其他部分解析在Spring源码中有,这里着重了解HandlerMapping什么时候注入的。
@Override
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
// Prepare this context for refreshing.
prepareRefresh();
// Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
--
//告诉子类刷新内部bean工厂。
--
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
5.obtainFreshBeanFactory
protected ConfigurableListableBeanFactory obtainFreshBeanFactory() {
refreshBeanFactory();
return getBeanFactory();
}
5.1 refreshBeanFactory (AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext类下)
@Override
protected final void refreshBeanFactory() throws BeansException {
--
//是否有beanfactory,有就清理掉
--
if (hasBeanFactory()) {
destroyBeans();
closeBeanFactory();
}
try {
--
//创建一个新的beanFactory
--
DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = createBeanFactory();
beanFactory.setSerializationId(getId());
--
//定制beanFactory
--
customizeBeanFactory(beanFactory);
--
重点
--
loadBeanDefinitions(beanFactory);
synchronized (this.beanFactoryMonitor) {
this.beanFactory = beanFactory;
}
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("I/O error parsing bean definition source for " + getDisplayName(), ex);
}
}
5.2 loadBeanDefinitions
@Override
protected void loadBeanDefinitions(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException, IOException {
// Create a new XmlBeanDefinitionReader for the given BeanFactory.
--
//为给定的BeanFactory创建一个新的XmlBeanDefinitionReader
--
XmlBeanDefinitionReader beanDefinitionReader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(beanFactory);
// Configure the bean definition reader with this context's
// resource loading environment.
beanDefinitionReader.setEnvironment(getEnvironment());
beanDefinitionReader.setResourceLoader(this);
beanDefinitionReader.setEntityResolver(new ResourceEntityResolver(this));
// Allow a subclass to provide custom initialization of the reader,
// then proceed with actually loading the bean definitions.
--
//初始化用于加载此上下文的bean定义的bean定义读取器。默认实现为空。
//可以在子类中重写,例如关闭XML验证或使用不同的XmlBeanDefinitionParser实现。
--
initBeanDefinitionReader(beanDefinitionReader);
--
//加载bean的定义信息
--
loadBeanDefinitions(beanDefinitionReader);
}
5.3loadBeanDefinitions
--
使用给定的XmlBeanDefinitionReader加载bean定义。
bean工厂的生命周期由refreshBeanFactory方法处理;
因此,该方法仅用于加载和/或注册bean定义。
委托给ResourcePatternResolver将位置模式解析到资源实例中
--
protected void loadBeanDefinitions(XmlBeanDefinitionReader reader) throws IOException {
--
//获取配置文件的路径信息
--
String[] configLocations = getConfigLocations();
if (configLocations != null) {
for (String configLocation : configLocations) {
--
加载配置文件信息
--
reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configLocation);
}
}
}
5.4 loadBeanDefinitions
@Override
public int loadBeanDefinitions(String location) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
return loadBeanDefinitions(location, null);
}
public int loadBeanDefinitions(String location, @Nullable Set<Resource> actualResources) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
ResourceLoader resourceLoader = getResourceLoader();
if (resourceLoader == null) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(
"Cannot load bean definitions from location [" + location + "]: no ResourceLoader available");
}
if (resourceLoader instanceof ResourcePatternResolver) {
// Resource pattern matching available.
try {
Resource[] resources = ((ResourcePatternResolver) resourceLoader).getResources(location);
--
加载bean
重点就这一个,此方法后beanfactory内就包含有很多HandleMapping等信息
---
int count = loadBeanDefinitions(resources);
---
if (actualResources != null) {
Collections.addAll(actualResources, resources);
}
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Loaded " + count + " bean definitions from location pattern [" + location + "]");
}
return count;
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(
"Could not resolve bean definition resource pattern [" + location + "]", ex);
}
}
else {
// Can only load single resources by absolute URL.
Resource resource = resourceLoader.getResource(location);
int count = loadBeanDefinitions(resource);
if (actualResources != null) {
actualResources.add(resource);
}
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Loaded " + count + " bean definitions from location [" + location + "]");
}
return count;
}
}
@Override
public int loadBeanDefinitions(Resource... resources) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
Assert.notNull(resources, "Resource array must not be null");
int count = 0;
for (Resource resource : resources) {
count += loadBeanDefinitions(resource);
}
return count;
}
//在这个类中,会将你编写的配置文件转换成流的形式
--
public int loadBeanDefinitions(EncodedResource encodedResource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
Assert.notNull(encodedResource, "EncodedResource must not be null");
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Loading XML bean definitions from " + encodedResource);
}
Set<EncodedResource> currentResources = this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.get();
if (currentResources == null) {
currentResources = new HashSet<>(4);
this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.set(currentResources);
}
if (!currentResources.add(encodedResource)) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(
"Detected cyclic loading of " + encodedResource + " - check your import definitions!");
}
try {
--
//将配置文件转成字节流
--
InputStream inputStream = encodedResource.getResource().getInputStream();
try {
InputSource inputSource = new InputSource(inputStream);
if (encodedResource.getEncoding() != null) {
inputSource.setEncoding(encodedResource.getEncoding());
}
--
//字节流文件传入
--
return doLoadBeanDefinitions(inputSource, encodedResource.getResource());
}
protected int doLoadBeanDefinitions(InputSource inputSource, Resource resource)
throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
try {
--
//加载成Document
--
Document doc = doLoadDocument(inputSource, resource);
--
//注册bean定义信息并返回结果数量
--
int count = registerBeanDefinitions(doc, resource);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Loaded " + count + " bean definitions from " + resource);
}
return count;
}
中间跳过两步方法的调用
5.5 解析xml配置文件
最后会来到这里
protected void parseBeanDefinitions(Element root, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) {
if (delegate.isDefaultNamespace(root)) {
NodeList nl = root.getChildNodes();
--
//一重循环,将转成字节流的文件取出
//在跳过的两步中,有对传入的字节流进行处理,然后转成Node类型
//每一个Node就是你编写的配置文件的空行、注释、配置的bean组件信息
//将每个Node和Element类型进行匹配
//像mvc ,context,bean这样的名称空间都是适配的
--
for (int i = 0; i < nl.getLength(); i++) {
Node node = nl.item(i);
if (node instanceof Element) {
Element ele = (Element) node;
if (delegate.isDefaultNamespace(ele)) {
parseDefaultElement(ele, delegate);
}
else {
--
//一般会进入这个方法,因为一般isDefaultNamespace都是false
--
delegate.parseCustomElement(ele);
}
}
}
5.6parseCustomElement
public BeanDefinition parseCustomElement(Element ele, @Nullable BeanDefinition containingBd) {
--
//获取解析到的组件的名称空间uri
//如:http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc
--
String namespaceUri = getNamespaceURI(ele);
if (namespaceUri == null) {
return null;
}
--
解析名称空间的uri,得到名称空间里附带的组件:如HandlerMapping;HandlerAdapter等
或者是自己标注的组件
--
NamespaceHandler handler = this.readerContext.getNamespaceHandlerResolver().resolve(namespaceUri);
if (handler == null) {
error("Unable to locate Spring NamespaceHandler for XML schema namespace [" + namespaceUri + "]", ele);
return null;
}
--
将解析得到的组件加入到BeanDefinitionMap中
--
return handler.parse(ele, new ParserContext(this.readerContext, this, containingBd));
}
解析名称空间的uri
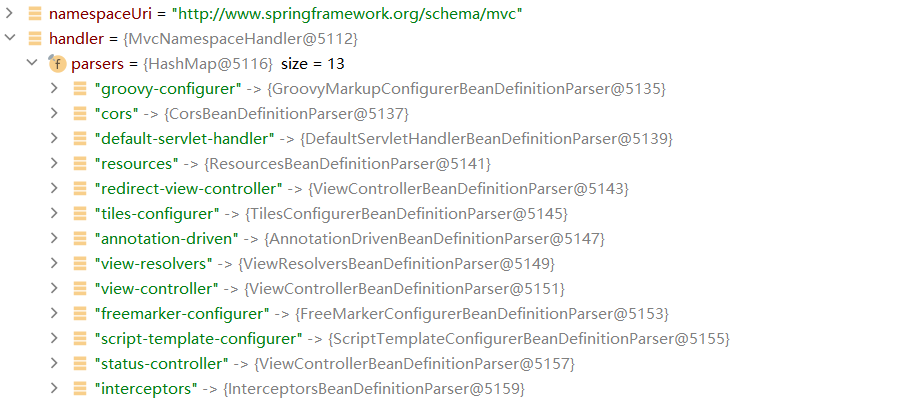
5.7 自己写的组件是如何扫描进来的?
public BeanDefinition parse(Element element, ParserContext parserContext) {
--
得到你标记的要扫描的包路径
--
String basePackage = element.getAttribute(BASE_PACKAGE_ATTRIBUTE);
basePackage = parserContext.getReaderContext().getEnvironment().resolvePlaceholders(basePackage);
String[] basePackages = StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray(basePackage,
ConfigurableApplicationContext.CONFIG_LOCATION_DELIMITERS);
// Actually scan for bean definitions and register them.
--
扫描组件bean并注册他们
--
ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner scanner = configureScanner(parserContext, element);
--
扫描注册你标记了注解的组件或者说你注册的组件,如Controller等
--
Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> beanDefinitions = scanner.doScan(basePackages);
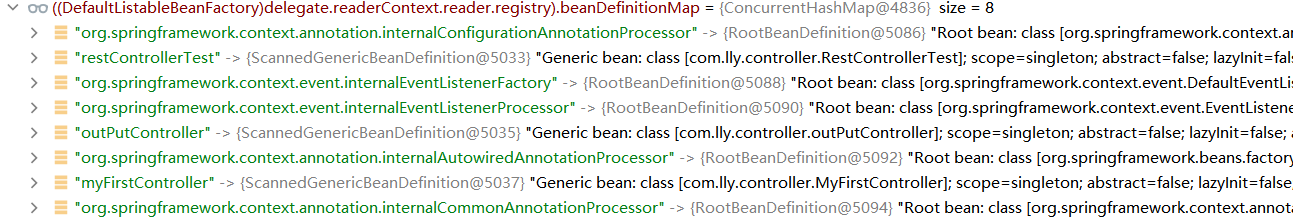
--
扫描component-scan中有的组件注册到beanDefinitions中,附图:
--
registerComponents(parserContext.getReaderContext(), beanDefinitions, element);
return null;
}
标记注解的组件加入:
5.8 某些HandlerMapping等是如何加进来的?
在AnnotationDrivenBeanDefinitionParser类下,
有public BeanDefinition parse(Element element, ParserContext context) {}这么一个方法
里面有一大段很长的一段实现。
里面要注册那些HandlerMapping;HandlerAdapter都是写好了的。
类似调用者样的方法:
RootBeanDefinition handlerMappingDef = new RootBeanDefinition(RequestMappingHandlerMapping.class);
readerContext.getRegistry().registerBeanDefinition(HANDLER_MAPPING_BEAN_NAME, handlerMappingDef);
这里是注册RequestMappingHandlerMapping
如果你单纯写了一个mvc的组件,里面会注册些什么,底层已经是写好了的。
** mvc:annotation-driven组件扫描注册后**

另附我的xml配置文件:
以上步骤只在我只有三个组件配置的情况下得出,其他原理应该大差不差
dispatch-servlet.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<!--扫描所有组件-->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.lly"/>
<!--注解生效-->
<mvc:annotation-driven/>
<!--配置一个视图解析器;能帮我们拼接页面地址-->
<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver">
<property name="prefix" value="/WEB-INF/pages/"/>
<property name="suffix" value=".jsp"/>
</bean>
</beans>
组件注册流程总结:
- Spring在启动的时候会逐个加载配置的xml文件,如applicationContext.xml;dispatcher-servlet.xml
- 如果你在web.xml中配置了组件,但建的文件的名字没写对应
- Spring会使用默认的名字(如:)并找对应目录下的的文件,如果你配置文件的组件名字和你的配置的文件名不一样,且你的组件文件命名又和官方的默认命名不一样,报错
- 在加载组件的时候会将组件转成字节流信息
- 解析字节流信息,并将信息封装成一个Node类型的数组
- 遍历这个数组,得到适合的类型
- 解析该类型得到uri地址,根据uri解析出该命名空间含有的组件
- 根据解析出的组件,选择出你配置文件有的组件进行组件注册
eg:localName=annotation-driven
- 至此,Spring启动的时候,组件的扫描完成,但此时只是加入到BeanDefinitionMap,后续还需通过initStrategies方法初始化到handlerMappings等List集合中。
- 即BeanDefinitionMap中保存的是所有的bean组件,后续还得通过初始化加入到对应的类型中。是handlerMappings或者是HandlerAdapter或者是其他。。。
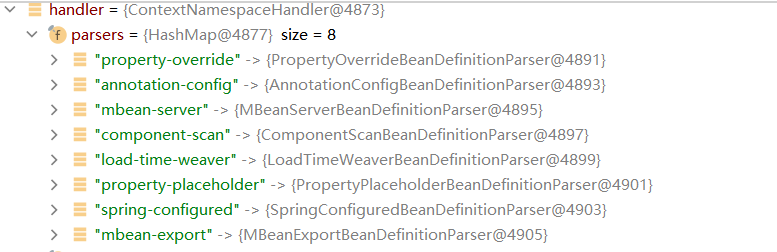
补充:如果你配置文件里的什么组件都没有,怎么办?

/**
* Initialize the strategy objects that this servlet uses.
* <p>May be overridden in subclasses in order to initialize further strategy objects.
*/
以下方法会实现组件的初始化,以initHandlerMappings举例
protected void initStrategies(ApplicationContext context) {
initMultipartResolver(context);
initLocaleResolver(context);
initThemeResolver(context);
initHandlerMappings(context);
initHandlerAdapters(context);
initHandlerExceptionResolvers(context);
initRequestToViewNameTranslator(context);
initViewResolvers(context);
initFlashMapManager(context);
}
initHandlerMappings
private void initHandlerMappings(ApplicationContext context) {
this.handlerMappings = null;
--
//detectAllHandlerMappings默认true,探查ApplicationContext里的HandlerMappings
--
if (this.detectAllHandlerMappings) {
// Find all HandlerMappings in the ApplicationContext, including ancestor contexts.
Map<String, HandlerMapping> matchingBeans =
BeanFactoryUtils.beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors(context, HandlerMapping.class, true, false);
--
//配置文件里什么都没有的话,为空
--
if (!matchingBeans.isEmpty()) {
this.handlerMappings = new ArrayList<>(matchingBeans.values());
// We keep HandlerMappings in sorted order.
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(this.handlerMappings);
}
}
else {
try {
HandlerMapping hm = context.getBean(HANDLER_MAPPING_BEAN_NAME, HandlerMapping.class);
this.handlerMappings = Collections.singletonList(hm);
}
catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) {
// Ignore, we'll add a default HandlerMapping later.
}
}
// Ensure we have at least one HandlerMapping, by registering
// a default HandlerMapping if no other mappings are found.
然后有这么个默认的实现
--
if (this.handlerMappings == null) {
--
//使用默认的策略配置
--
this.handlerMappings = getDefaultStrategies(context, HandlerMapping.class);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("No HandlerMappings declared for servlet '" + getServletName() +
"': using default strategies from DispatcherServlet.properties");
}
}
}
getDefaultStrategies
protected <T> List<T> getDefaultStrategies(ApplicationContext context, Class<T> strategyInterface) {
--
//获取strategyInterface的名字handlerMapping,
//去配置文件中找默认的策略实现,这个配置文件在和DispatcherServlet类同级目录下的
//DispatcherServlet.properties中
String key = strategyInterface.getName();
String value = defaultStrategies.getProperty(key);
--
//以下进行策略装配
--
if (value != null) {
String[] classNames = StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray(value);
List<T> strategies = new ArrayList<>(classNames.length);
for (String className : classNames) {
try {
Class<?> clazz = ClassUtils.forName(className, DispatcherServlet.class.getClassLoader());
Object strategy = createDefaultStrategy(context, clazz);
strategies.add((T) strategy);
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new BeanInitializationException(
"Could not find DispatcherServlet's default strategy class [" + className +
"] for interface [" + key + "]", ex);
}
catch (LinkageError err) {
throw new BeanInitializationException(
"Unresolvable class definition for DispatcherServlet's default strategy class [" +
className + "] for interface [" + key + "]", err);
}
}
return strategies;
}
else {
return new LinkedList<>();
}
}
DispatcherServlet.properties

但最后发送请求的时候也是会报错的
因为虽然有了这些组件,但在doDispatch里进行getHandler或者getHandlerAdapter时也会报错
除非进行一些别的配置文件配置,比如注册bean组件
<bean name="hello" class="com.lly.controller.MyFirstController">
</bean>
MyFirstController
@Controller
public class MyFirstController{
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public String hello() {
System.out.println("处理hello请求....");
return "/WEB-INF/pages/success.jsp";
}
